https://github.com/gboysking/serverless-framework-basic/tree/master/dynamodb
GitHub - gboysking/serverless-framework-basic
Contribute to gboysking/serverless-framework-basic development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
In this blog post, we will create a simple device data storage application using AWS DynamoDB and Express. We will demonstrate how to design a database schema, create a custom table class for interacting with DynamoDB, and implement API routes to store and retrieve device data.
1. Introduction
DynamoDB is a highly scalable and low-latency NoSQL database provided by AWS. In this tutorial, we will create a simple device data storage application that allows us to store and retrieve data from multiple devices and device types. We will use Node.js with the Express web framework to build the backend and the AWS SDK for JavaScript to interact with DynamoDB.
2. Setting up the Environment
Before we begin, make sure you have Node.js installed on your system. You can download it from here.
After installing Node.js, create a new folder for your project and navigate to it using the command line. Initialize the project with npm:
npm init -y
Install the required libraries:
npm install express @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb @aws-sdk/lib-dynamodb
3. Designing the Database Schema
Our application will store device data in a DynamoDB table with the following schema:
- device_id_type: A string composed of the device ID and type, separated by a '#', which will serve as the hash key
- timestamp: A number representing the timestamp of the data, which will serve as the range key
Here's the schema definition in code:
AttributeDefinitions: [
{
AttributeName: 'device_id_type',
AttributeType: 'S',
},
{
AttributeName: 'timestamp',
AttributeType: 'N',
},
],
KeySchema: [
{
AttributeName: 'device_id_type',
KeyType: 'HASH',
},
{
AttributeName: 'timestamp',
KeyType: 'RANGE',
},
],
4. Creating the BaseDynamoDBTable Class
In this step, we will create a BaseDynamoDBTable class to handle the common tasks for interacting with DynamoDB tables. This class will be responsible for creating the table if it does not exist, waiting for the table to be ready, and providing a simple interface for interacting with the table.
The BaseDynamoDBTable class will have the following methods:
- onReady(): Wait for the table to be ready
- generateSchema(): Create the table schema
- createTableIfNotExists(): Create the table if it does not already exist
5. Implementing the DeviceDataTable Class
The DeviceDataTable class will extend the BaseDynamoDBTable class and provide additional methods for storing, retrieving, and deleting device data. These methods will include:
- putItem(): Store a new item in the table
- getItems(): Retrieve items based on device ID, type, and a time range
- deleteItem(): Delete an item from the table
6. Setting Up Express and Creating API Routes
We will use Express to create a simple API server that accepts requests to store and retrieve device data. First, create a new file called app.js and set up the basic Express server.
Next, import the DeviceDataTable class and create a new instance of it, passing in the table name as an option.
Finally, implement the following routes:
- POST /device_data: Store device data
- The body of the request should include device_id, type, timestamp, and any additional data
- GET /device_data: Retrieve device data for a specific device and type within a time range
- The query parameters should include device_id, type, start_time, and end_time
- DELETE /device_data: Delete a specific device data entry
- The query parameters should include device_id, type, and timestamp
7. Running the Application with Serverless Framework
To run the application using Serverless Framework offline, first ensure you have the Serverless Framework installed and set up on your system. If not, install it globally using the following command:
npm install -g serverless
Next, you'll need to install the serverless-offline plugin as a development dependency in your project:
npm install --save-dev serverless-offline
Create a serverless.yml configuration file in the root of your project and add the following configuration:
service: dynamodb
useDotenv: true
plugins:
- serverless-esbuild
- serverless-offline
custom:
serverless-offline:
httpPort: 3000
provider:
name: aws
runtime: nodejs16.x
lambdaHashingVersion: 20201221
memorySize: 128
timeout: 5
stage: dev
region: ap-northeast-2
environment:
STAGE: ${self:provider.stage}
functions:
app:
handler: src/handler.app_handler
events:
- http:
path: /app/{proxy+}
method: ANY
cors: true
In your app.js, export the handler function that will be used by the Serverless Framework:
module.exports.handler = serverless(app);
Now, you can run your application using the following command:
sls offline start
Your Express server will start listening on the default port 3000, and you can use a tool like Postman or curl to test the API endpoints.

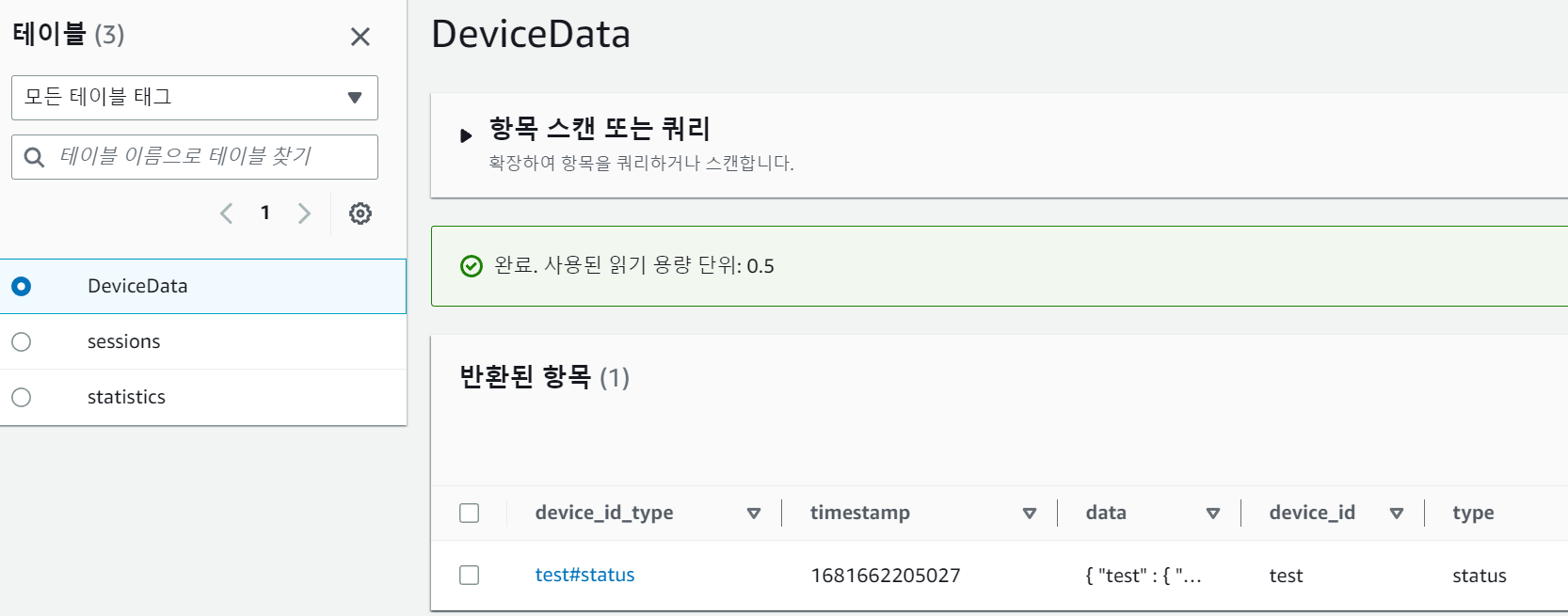
8. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we've demonstrated how to build a simple device data storage application using DynamoDB and Express. We designed a database schema, created a custom table class for interacting with DynamoDB, and implemented API routes to store, retrieve, and delete device data. We also showed how to run the application using Serverless Framework's offline mode for local testing. This example can serve as a foundation for building more complex applications that require efficient storage and retrieval of time-series data.
This article was written with the help of ChatGPT.
'ChatGPT > AWS Serverless' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS][DynamoDB] DynamoDB에서의 분산 Lock 소개 - 1 (0) | 2023.06.10 |
|---|---|
| [OpenAI][ChatGPT] Session Manager with TypeScript and AWS DynamoDB (0) | 2023.04.17 |
| [Serverless][DynamoDB] Time Series Statistics Manager (0) | 2023.04.13 |
| [Serverless][MySQL] Express Session Store (0) | 2023.04.12 |
| [Serverless][DynamoDB] Express Session Store (0) | 2023.04.12 |


